
Step 1: Learn the Basic Symbols of Notation
Music is made up of a variety of symbols, the most basic of which are the staff, the clefs and the notes. All music contains these fundamental components, and in order to learn how to read music, you must first familiarize yourself with these basics.
The Staff
The staff consists of five lines and four spaces. Each of those lines and each of those spaces represents a different letter, which in turn represents a note. Those lines and spaces represent notes named A-G, and the note sequence moves alphabetically up the staff.

Treble Clef
There are two main clefs with which to familiarize yourself; the first is a treble clef. The treble clef has the ornamental letter G on the far left side. The G’s inner swoop encircles the “G” line on the staff. The treble clef notates the higher registers of music, so if your instrument has a higher pitch, such as a flute, violin or saxophone, your sheet music is written in the treble clef. Higher notes on a keyboard also are notated on the treble clef.

Notes
Notes placed on the staff tell us which note letter to play on our instrument and how long to play it. There are three parts of each note, the note head, the stem and the flag.

Every note has a note head, either filled (black) or open (white). Where the note head sits on the staff (either on a line or a space) determines which note you will play. Sometimes, note heads will sit above or below the five lines and four spaces of a staff. In that case, a line is drawn through the note, above the note or below the note head, to indicate the note letter to play, as in the B and C notes above.
The note stem is a thin line that extends either up or down from the note head. The line extends from the right if pointing upward or from the left if pointing downward. The direction of the line doesn’t affect how you play the note, but serves as a way to make the notes easier to read while allowing them to fit neatly on the staff. As a rule, any notes at or above the B line on the staff have downward pointing stems, those notes below the B line have upward pointing stems.
The note flag is a curvy mark to the right of the note stem. Its purpose is to tell you how long to hold a note. We’ll see below how a single flag shortens the note’s duration, while multiple flags can make it shorter still.
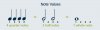
Now that you know the parts to each note, we’ll take a closer look at those filled and open note heads discussed above. Whether a note head is filled or open shows us the note’s value, or how long that note should be held. Start with a closed note head with a stem. That’s our quarter note, and it gets one beat. An open note head with a stem is a half note, and it gets two beats. An open note that looks like an “o” without a stem is a whole note, and it gets held for four beats.

There are other ways to extend the length of a note. A dot after the note head, for example, adds another half of that note’s duration to it. So, a half note with a dot would equal a half note and a quarter note; a quarter note with a dot equals a quarter plus an eighth note. A tie may also be used to extend a note. Two notes tied together should be held as long as the value of both of those notes together, and ties are commonly used to signify held notes that cross measures or bars.

Step 2: Pick Up the Beat
In order to play music, you need to know its meter, the beat you use when dancing, clapping or tapping your foot along with a song. When reading music, the meter is presented similar to a fraction, with a top number and a bottom number, we call this the song’s time signature. The top number tells you how many beats to a measure, the space of staff in between each vertical line (called a bar). The bottom number tells you the note value for a single beat, the pulse your foot
taps along with while listening.

In the example above, the time signature is 4/4, meaning there are 4 beats per bar and that every quarter note gets one beat. and try counting along 1,2,3,4 – 1,2,3,4 with the beat numbers above.
In the example below, the time signature is 3/4, meaning there are 3 beats per bar and that every quarter note gets one beat, try counting the beats, 1,2,3 – 1,2,3.
In addition to your note values and time signature, the last piece to feeling the rhythm is knowing your tempo, or beats per minute. Tempo tells you how fast or slow a piece is intended to be played, and often is shown at the top of a piece of sheet music. A tempo of, say 60 BPM (beats per minute) would mean you’d play 60 of the signified notes every minute or a single note every second. Likewise, a tempo of 120 would double the speed at 2 notes every second. You may also see Italian words like “Largo,” “Allegro” or “Presto” at the top of your sheet music, which signify common tempos. Musicians use a tool, called a metronome, to help them keep tempo while practicing a new piece
metronome - http://a.bestmetronome.com/
